屏幕自动旋转与手动旋转总结
iOS 的屏幕旋转有很多弯弯绕的地方, 旋转的成功与否取决于多个层面的共同作用.
横竖屏设置的地方
AppDelegate.swiftswift// 自定义属性, 用于控制全局旋转方向 var interfaceOrientations: UIInterfaceOrientationMask = .portrait func application(_ application: UIApplication, supportedInterfaceOrientationsFor window: UIWindow?) -> UIInterfaceOrientationMask { return interfaceOrientations }Info.plist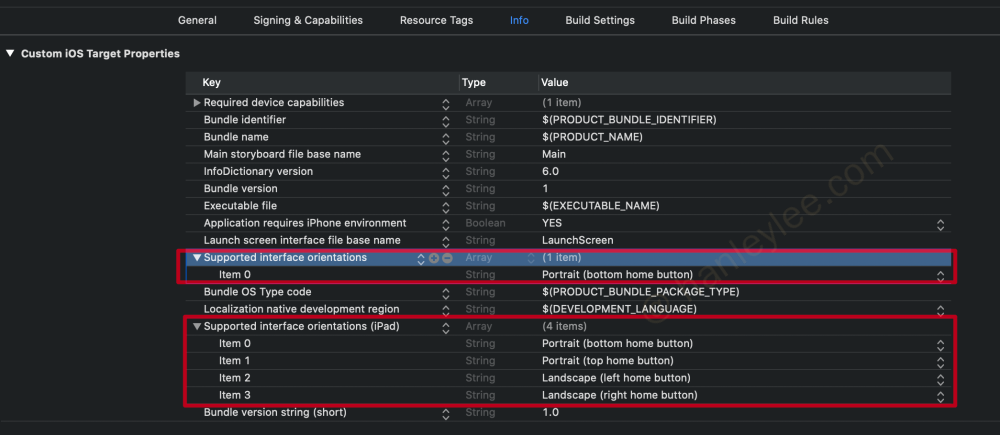
VC.swiftswift/// 自动旋转的变量 (用于设置只读属性 shouldAutoratate) private var shouldAutorotateVariable = false private var supportOrientations: UIInterfaceOrientationMask = [.landscapeLeft, .landscapeLeft, .portrait] // 是否支持自动转屏 override open var shouldAutorotate: Bool { get { return shouldAutorotateVariable } set { shouldAutorotateVariable = newValue } } // 本 vc 所支持的转动方向 override var supportedInterfaceOrientations: UIInterfaceOrientationMask { get { return supportOrientations } set { supportOrientations = newValue } } override var preferredInterfaceOrientationForPresentation: UIInterfaceOrientation { return .landscapeRight }
shouldAutoratate 与旋转级别
要理解各个 VC 的控制关系, 首先要理清最重要的 VC 中的 shouldAutoratate 属性的设置
如果某个
VC中的shouldAutorotate被设置为false, 那么系统将忽略下面的设置:UIApplicationDelegate中的supportedInterfaceOrientationsForWindow:方法- 该
VC通过supportedInterfaceOrientations方法设置的自己支持的屏幕方向
系统只考虑用户在 “
Info.plist中的设置.如果某个
VC中的shouldAutorotate未被重写 (或者被重写为true, 因为默认值就是true), 那么系统将优先考虑使用下面两个设置的交集:UIApplicationDelegate中的supportedInterfaceOrientationsForWindow: 方法 (默认不实现, 即不支持任何方向)- 该
VC通过supportedInterfaceOrientations方法设置的自己支持的屏幕方向 (默认不实现, 即支持任何方向)
如果以上两个设置只有其中一种, 就按照他们的默认行为来进行判断; 如果没有以上两个设置, 再使用 “
Info.plist中的设置. 因此, 我们有时可能会有一种UIApplicationDelegate中的方法会覆写Info.plist设置的错觉切记注意: 如果两个方法都设置了且没有任何交集, 那么有崩溃的风险!
常见问题
shouldAutoratate为什么不走正常情况下屏幕旋转时会访问
VC中的shouldAutorotate属性, 断点会走这里; 但是很多人都会发现这个断点不走这个属性了, 问题的根源就在于继承上:- 如果不在根控制器 (
UITabBarController和UINavigationController) 中设置那 3 个方法,VC中重写shouldAutorotate是不会被调用的. - 如果在根控制器中设置了那三个方法, 那么第一个控制器的
shouldAutorotate能调用, 但是往下push的控制器中的shouldAutorotate就不调用了, 不管勾选没勾选横屏. - 如果
modal一个没有实现上面三个方法的UINavigationController控制器, 那么新控制器的shouldAutorotate也是不能调用 - 如果
modal一个普通的viewController, 控制器中的shouldAutorotate能被调用 - 如果
modal一个自定义转场的控制器, 不能调用
- 如果不在根控制器 (
一定要监听
UIApplication.didChangeStatusOrientationNotification必须要监听
UIApplication.didChangeStatusOrientationNotification而不是UIDevice.orientationDidChangeNotification, 原因有下:UIDevice的通知会在从后台进入前台时调用三次, 具体原因不明UIDevice会有多个方向的通知, 比如从faceUp转向landscapeLeft时也会发出一个通知, 但这是我们一般是不需要这个通知的
一定要使用
UIApplication.shared.statusBarOrientation来判断方向我们也可以使用
UIDevice.current.orientation来判断当前设备的方向, 这个方向的类别是UIDeviceOrientation, 其一共有如下可能:unknownportraitportraitUpsideDownlandscapeLeftlandscapeRightfaceUpfaceDown
这非常不利于我们对方向的判断, 我们只想要当前设备的屏幕方向到底是横向还是竖向, 因此使用
UIApplication.shared.statusBarOrientation是最好的选择, 他的类别是UIInterfaceOrientationMask, 共有如下可能:portraitlandscapeLeftlandscapeRightportraitUpsideDownlandscapeallallButUpsideDown
屏幕旋转的重新约束
如果 UI 元素使用了 autoLayout, 那么在屏幕旋转后其布局依然是遵守 autoLayout 的, 但是如果是使用 frame 的绝对布局, 那么一定要重新进行布局, 可以在 VC 的
layoutSubviews或 view 的viewWillLayoutSubviews方法中根据横竖屏判断进行重新布局, 也可以在旋转监听方法中写布局改变的代码
屏幕事件处理代码示例
let appdelegate = UIApplication.shared.delegate as! AppDelegate
// 监听屏幕旋转事件
NotificationCenter.default.rx.notification(UIApplication.didChangeStatusBarOrientationNotification)
.subscribe(onNext: { [weak self] (_) in
guard let self = self, UIViewController.topMost == self else {return} // 控制仅最前端为自己时才会触发改变元素方法
self.changeElementsWhenRotate(showLock: true)
})
.disposed(by: disposeBag)
/// 显示横屏与竖屏的逻辑 (添加移除相关 view)
///
/// - Parameter showLock: 是否显示锁定界面, 因为要隐藏 tabbar, 进入个股详情后再退回到本页面会自动显示底部 tabBar,
/// 因此要在 viewWillAppear 中调用本方法, 并且不显示锁定框
private func changeElementsWhenRotate(showLock: Bool) {
guard let wtVC = vcDic[.wt] as? QTWTMainVC else { return }
wtVC.popView.removeFromeSuperview()
wtVC.menuBtn.tintColor = UIColor(hex: 0xB3B3B3)
/// 菜单栏高度
var menuHeight: CGFloat = 0.0
/// 跑马灯高度
var marqueHeight: CGFloat = 0.0
if UIApplication.shared.statusBarOrientation.isLandscape {
self.lockToastView.isHidden = !showLock
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: DispatchTime.now() + 2) {
self.lockToastView.isHidden = true
}
navigationController?.setNavigationBarHidden(true, animated: false)
unlockBtn.isHidden = false
self.tabBarController?.tabBar.isHidden = true
wtVC.noLoginView.isHidden = true
menuHeight = 0.0
wtVC.menuBtn.isHidden = true
marqueHeight = 0.0
} else {
navigationController?.setNavigationBarHidden(false, animated: false)
self.lockToastView.isHidden = true
self.lockSuccessView.isHidden = true
unlockBtn.isHidden = true
tabBarController?.tabBar.isHidden = false
wtVC.noLoginView.isHidden = userM.isLogon ? true : false
wtVC.menuBtn.isHidden = false
menuHeight = 40.0
marqueHeight = 30.0
}
wtVC.menuView.snp.remakeConstraints { make in
make.top.equalToSuperview()
make.left.equalToSuperview().offset(13)
make.right.equalToSuperview().offset(-80.0)
make.height.equalTo(menuHeight)
}
/// 若存在跑马灯, 则将跑马灯高度设为零并且本身 view 距顶部设为零
if let parent = parent as? BaseMarqueeController, let marque = parent.marqueeView {
marqueHeight = (marque.isRunning || marque.isPaused) ? marqueHeight : 0.0 // 在跑马灯运行期间, 仍然使用跑马灯自身的高度 30, 否则为 0
marque.isHidden = marqueHeight == 0.0 ? true : false // 本步骤隐藏之后即可不使用下一步骤的重新布局, 加上是双重保险
marque.snp.remakeConstraints {(make) in
make.top.left.right.equalToSuperview()
make.height.equalTo(marqueHeight)
}
self.view.snp.remakeConstraints {(make) in
make.top.equalTo(marqueHeight)
make.left.right.bottom.equalToSuperview()
}
}
subviews.enumerated().forEach { (index, view) in
view.snp.remakeConstraints {(make) in
make.top.height.width.equalToSuperview()
make.left.equalToSuperview().offset(UIDevice.ck.width * CGFloat(index))
}
}
// 保证在旋转屏幕后得到正确的子 VC 布局
wtVC.containerVcs.forEach {(type, vc) in
vc.view.snp.remakeConstraints {(make) in
make.left.equalTo(UIDevice.ck.width * CGFloat(type.index))
make.top.equalToSuperview()
make.width.equalTo(UIDevice.ck.width)
make.height.equalToSuperview()
}
}
scrollView.setContentOffset(CGPoint(x: self.scrollView.bounds.width * CGFloat(quotationType.index), y: 0), animated: false)
wtVC.scrollView.setContentOffset(CGPoint(x: CGFloat(wtVC.selectedVCType.index) * UIDevice.ck.width, y: 0), animated: false)
}
// 强制旋转屏幕
unlockBtn.rx.tap
.subscribe(onNext: { [weak self] (_) in
guard let self = self else {return}
self.unlockBtn.isHidden = true
self.appdelegate.interfaceOrientations = .all
self.isLocked = false
UIDevice.current.setValue(UIInterfaceOrientation.portrait.rawValue, forKey: "orientation")
if UIDevice.current.orientation == .portrait { // 特殊情况: 锁定后在竖屏状态下解锁
UIViewController.attemptRotationToDeviceOrientation()
self.showLandscape()
}
})
.disposed(by: disposeBag)
headerView.buttonRotate.rx.tap
.subscribe(onNext: { (_) in
UIDevice.current.setValue(UIInterfaceOrientation.landscapeRight.rawValue, forKey: "orientation")
UIViewController.attemptRotationToDeviceOrientation()
})
.disposed(by: disposeBag)
// 强制锁定屏幕
lockSuccessView.tapGesture.rx.event
.subscribe(onNext: { [weak self] (_) in
guard let self = self else {return}
self.lockSuccessView.isHidden = true
switch UIDevice.current.orientation {
case .landscapeLeft: self.appdelegate.interfaceOrientations = .landscapeRight
case .landscapeRight: self.appdelegate.interfaceOrientations = .landscapeLeft
default: break
}
})
.disposed(by: disposeBag)参考
本博客文章采用 CC 4.0 协议,转载需注明出处和作者。
