Git 的一些实际使用技巧

本篇文章列举了一些 Git 实际使用技巧, 如果你喜欢终端 Git 操作, 那这就是为你准备的!
加速 git 资源下载
由于各种原因, GitHub 虽然在国内可以访问, 但是速度非常不理想, 可以考虑使用以下任一方式进行加速
ghproxy
使用方式:
git clone https://ghproxy.com/https://github.com/stilleshan/ServerStatuswget https://ghproxy.com/https://github.com/stilleshan/ServerStatus/archive/master.zipwget https://ghproxy.com/https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stilleshan/ServerStatus/master/Dockerfilecurl -O https://ghproxy.com/https://github.com/stilleshan/ServerStatus/archive/master.zipcurl -O https://ghproxy.com/https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stilleshan/ServerStatus/master/Dockerfile
fastgit
- 下载仓库: 将
github.com替换为hub.fastgit.xyztxtgit clone https://github.com/hanleylee/dotsh.git -> git clone https://hub.fastgit.org/hanleylee/dotsh.git - 下载文件: 将
raw.githubusercontent.com替换为raw.fastgit.orgtxtwget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/hanleylee/dotsh/main/README.md -> wget https://raw.fastgit.org/hanleylee/dotsh/main/README.md
jsdelivr
也可以使用 jsdelivr 的 cdn 进行国内网络加速下载, 同样也是对链接进行改造:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/hanleylee/dotsh/README.md -> wget https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/hanleylee/dotsh/README.md本工具的限制是只能下载文件, 不能下载整个仓库
更改系统 hosts 文件
更改系统 hosts 文件, 编辑 /etc/hosts, 加入一条 host 记录:
199.232.96.133 raw.githubusercontent.com上面的 IP 地址是 githubusercontent.com 对应的 ip 地址之一, ip 地址可能会随时间变化, 最新地址可以在 这里 查看.
使用 Git 管理大文件
Git LFS (Large File Storage) is a Git extension developed by Atlassian, GitHub, and a few other open source contributors, that reduces the impact of large files in your repository by downloading the relevant versions of them lazily.
在游戏开发过程中, 设计资源占用了很大一部分空间. 像 png, psd 等文件是二进制 (blob) 的, 体积也很庞大. 但 git 的 diff / patch 等是基于文件行的. 对于二进制文件来说. git 需要存储每次 commit 的改动. 每次当二进制文件修改, 发生变化的时候. 都会产生额外的提交量. 导致 clone 和 pull 的数据量大增. 在线仓库的体积也会迅速增长.
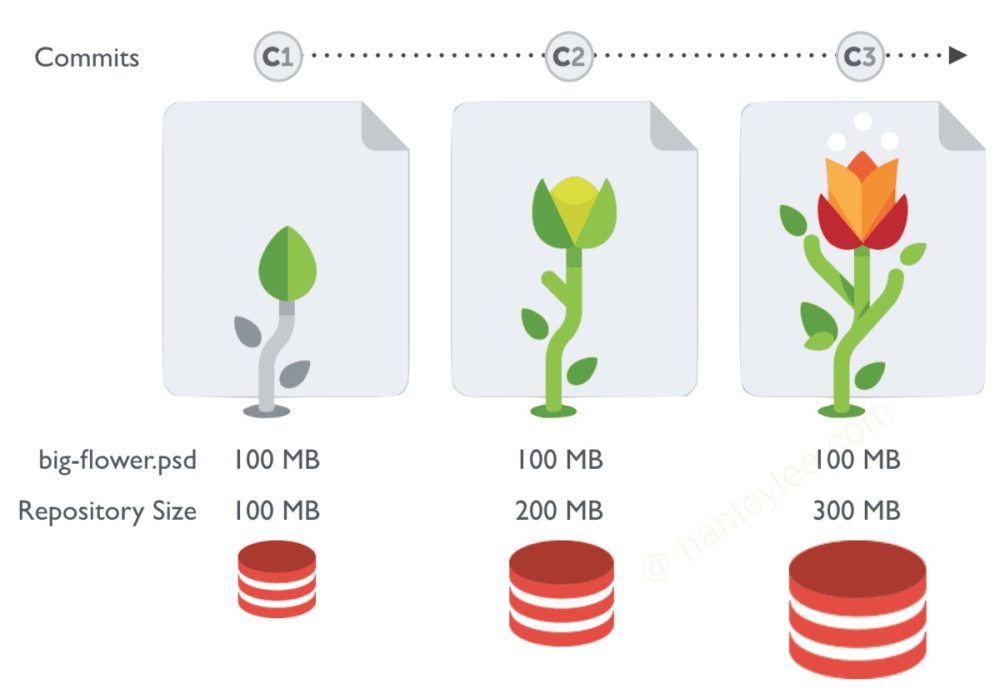
LFS(Large File Storage) 就是为了解决这一问题而产生的工具. 它将你所标记的大文件保存至另外的仓库, 而在主仓库仅保留其轻量级指针. 么在你检出版本时, 根据指针的变化情况下更新对应的大文件. 而不是在本地保存所有版本的大文件
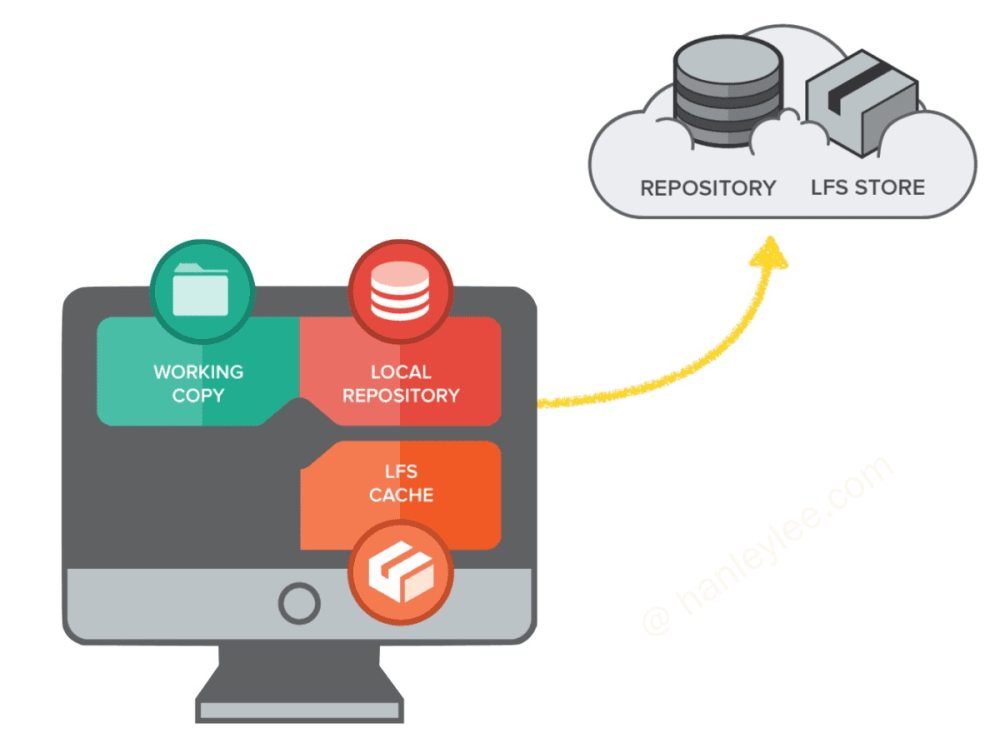
安装
brew install git-lfs使用
git lfs install: 为当前 repo 开启大文件支持, 这将在你的仓库中安装一个特殊的 pre-push Git 钩子, 该钩子将在你执行 git push 的时候传输 Git LFS 文件到服务器上git lfs track *.pdf: 为当前路径下的所有文件开启大文件追踪git lfs track "*.pdf": 只追踪*.pdf文件git lfs track **/*: 为当前 repo 内当前路径下所有文件及子文件夹下所有文件开启大文件追踪git lfs ls-files: 列出当前所有追踪的大文件git lfs clone: 安装 Git LFS 后, 你可以像往常一样使用 git clone 命令来克隆 Git LFS 仓库. 在克隆过程的结尾, Git 将检出默认分支 (通常是 master), 并且将自动为你下载完成检出过程所需的所有 Git LFS 文件. 如果你正在克隆包含大量 LFS 文件的仓库, 显式使用 git lfs clone 命令可提供更好的性能, git lfs clone 命令不会一次下载一个 Git LFS 文件, 而是等到检出 (checkout) 完成后再批量下载所有必需的 Git LFS 文件. 这利用了并行下载的优势, 并显著减少了产生的 HTTP 请求和进程的数量git lfs pull: 就像克隆一样, 你可以使用常规的 git pull 命令拉取 Git LFS 仓库. 拉取完成后, 所有需要的 Git LFS 文件都会作为自动检出过程的一部分而被下载. 不需要显式的命令即可获取 Git LFS 内容. 然而, 如果检出因为意外原因而失败, 你可以通过使用 git lfs pull 命令来下载当前提交的所有丢失的 Git LFS 内容git lfs prune: 删除所有被认为是旧的本地 git lfs 文件--dry-run: 空运行, 不真实执行, 仅观察将会产生何种结果--verbose: 详细过程输出
提交代码需要将 gitattributes 文件提交至仓库. 它保存了文件的追踪记录
将 git lfs track 的文件转换为正常 git 管理的文件
git lfs untrack <file>
git rm --cached <file>
git add <file>
git commit -m "restore file" to git from lfsFaster way to get git branch
我们可以通过 git symbolic-ref --short -q HEAD 来获取当前方式, 但是效率有点低, 可以尝试使用如下 shell 脚本快速获取
function _get_git_branch() {
local _head_file _head
local _dir="$PWD"
while [[ -n "$_dir"]]; do
_head_file="$_dir/.git/HEAD"
if [[ -f "$_dir/.git"]]; then
read -r _head_file < "$_dir/.git" && _head_file="$_dir/${_head_file#gitdir: }/HEAD"
fi
[[ -e "$_head_file"]] && break
_dir="${_dir%/*}"
done
if [[ -e "$_head_file"]]; then
read -r _head < "$_head_file" || return
case "$_head" in
ref:*) printf "${_head#ref: refs/heads/}";;
"");;
# HEAD detached
*) printf "${_head:0:9}";;
esac
return 0
fi
return 1
}使用裸仓库在多台电脑上同步配置文件
- 创建裸仓库并配置bash
git init --bare $HOME/.hlconfig.git echo 'alias hlconfig="/usr/bin/git --git-dir=$HOME/.hlconfig.git/ --work-tree=$HOME"' >> $HOME/.zshrc source ~/.zshrc hlconfig config --local status.showUntrackedFiles no - 将配置文件添加到此裸仓库中bash
hlconfig status hlconfig add .vimrc hlconfig commit -m "Add vimrc" hlconfig remote add origin https://www.github.com/username/repo.git hlconfig push origin master - 在另一台机器上 clone 此裸仓库并覆盖配置bash
echo 'alias hlconfig="/usr/bin/git --git-dir=$HOME/.hlconfig.git/ --work-tree=$HOME"' >> $HOME/.zshrc source ~/.zshrc echo ".hlconfig.git" >> $HOME/.gitignore_global git clone --bare https://www.github.com/username/repo.git $HOME/.hlconfig.git hlconfig config --local status.showUntrackedFiles no hlconfig checkouthlconfig checkout 的时候, 如果另一台机器上已经有了相关配置文件的话会提示失败, 需要移动这些文件到另一处, 或者使用
hlconfig checkout -f强制覆写这些文件
在 hlconfig add 了需要同步的配置文件后, 如果配置文件被修改了, 我们可以通过:
hlconfig add -u来添加更新的内容到git中hlconfig commit -a直接将修改的内容进行commit切记不可以使用
hlconfig add.或hlconfig add -A, 因为这两个命令是等价的, 会将本仓库路径控制下的所有新文件, 修改文件, 删除文件添加到版本管理中, 由于我们的裸仓库的管理目录是$HOME, 因此会把此目录下的所有文件添加到版本管理中, 这并不是我们想要的结果.(当然我们可以为此裸仓库配置.gitignore文件以规避此种问题, 但是与本裸仓库的使用理念又不同了)
为什么要使用裸仓库而不是普通仓库来管理
本例中创建的仓库是 .hlconfig.git, 是一个裸仓库, 因为是裸仓库, 因此
- 没有工作区, 其内没有
.git文件夹 - 文件夹内的内容直接是
.git文件夹的所有内容. - 在指定了
git-dir与work-tree后能管理此电脑上的所有文件 - 仓库可以放在电脑上的任意位置
如果使用普通仓库来管理:
- 必须在
$HOME中直接建立仓库, 目的是将所有$HOME作为工作区
裸仓库与普通仓库
git init repo 初始化一个正常仓库, git init repo.git --bare 初始化一个裸仓库.
裸仓库不包含工作区, 不能直接在裸仓库目录下使用 git status, git add 等常用的命令. 因为不包含工作区, 因此只会记录 git 的提交历史, 当前 head, branch 等基本信息, 这样特别适合与在服务端创建用来接收 push 的公共仓库.
归根到底, 最大的区别就是 裸仓库直接将 .git 文件夹中的内容取出放到了裸仓库的根目录下
普通仓库 (test1) 与裸仓库 (test2) 的目录结构对比:
hanley ~/Desktop/repotest
# Initialized empty Git repository in /Users/hanley/Desktop/repotest/test1/.git/
$ git init test1
hanley ~/Desktop/repotest
$ git init test2 --bare
Initialized empty Git repository in /Users/hanley/Desktop/repotest/test2/
hanley ~/Desktop/repotest
$ tree -a
.
├──.DS_Store
├── test1
│ └──.git
│ ├── HEAD
│ ├── config
│ ├── description
│ ├── hooks
│ │ ├── applypatch-msg.sample
│ │ ├── commit-msg.sample
│ │ ├── fsmonitor-watchman.sample
│ │ ├── post-update.sample
│ │ ├── pre-applypatch.sample
│ │ ├── pre-commit.sample
│ │ ├── pre-merge-commit.sample
│ │ ├── pre-push.sample
│ │ ├── pre-rebase.sample
│ │ ├── pre-receive.sample
│ │ ├── prepare-commit-msg.sample
│ │ └── update.sample
│ ├── info
│ │ └── exclude
│ ├── objects
│ │ ├── info
│ │ └── pack
│ └── refs
│ ├── heads
│ └── tags
└── test2
├── HEAD
├── config
├── description
├── hooks
│ ├── applypatch-msg.sample
│ ├── commit-msg.sample
│ ├── fsmonitor-watchman.sample
│ ├── post-update.sample
│ ├── pre-applypatch.sample
│ ├── pre-commit.sample
│ ├── pre-merge-commit.sample
│ ├── pre-push.sample
│ ├── pre-rebase.sample
│ ├── pre-receive.sample
│ ├── prepare-commit-msg.sample
│ └── update.sample
├── info
│ └── exclude
├── objects
│ ├── info
│ └── pack
└── refs
├── heads
└── tags正常仓库与裸仓库的 config 文件对比
- 正常仓库bash
[core] repositoryformatversion = 0 filemode = true bare = false logallrefupdates = true ignorecase = true precomposeunicode = true - 裸仓库bash
[core] repositoryformatversion = 0 filemode = true bare = true ignorecase = true precomposeunicode = true
可以看到最直观的差异在于 bare 配置项是否为 true, 此外不加裸仓库配置中有一项 logallrefupdates = true, 作用根据名字就可以看出来, 记录所有的 ref (引用) 更新.
此外, 如果我们想在本地使用裸仓库作为管理 $HOME 的仓库, 可以通过指定 git 目录, 指定工作路径的方式来实现 git status 命令:
git --git-dir=/Users/hanley/.hlconfig.git/ --work-tree=/Users/hanley status解决合并冲突的步骤
- 在合并时产生了冲突
- 使用
git mergetool工具对冲突文件逐个修改, 或者使用gui工具进行修改txt<<<<<<< 到 ======= 是在当前分支合并之前的文件内容 ======= 到》>>>>> psr/psr-02 是在其它分支下修改的内容 需要在这个两个版本中选择一个, 然后把标记符号也要一起删除 git add经过修改后的文件git commit&&git push
恢复一个彻底删掉的 commit
git reflog
git log HEAD@{6}\n: 1415211713:0;git log HEAD@{6}
git reflog HEAD@{6}
git reset --hard HEAD@{6}判断一个 commit 是否属于某个 branch
可以使用 git branch --contains $COMMIT_ID | grep -E '(^|\s)branch$' &>/dev/null
或者使用 git merge-base --is-ancestor $COMMIT_ID $BRANCH, 这种方式更优
规范化提交 commit
可以在 ~/.gitconfig 中配置全局 commit 模板:
[commit]
template = /Users/hanley/.stCommitMsg然后在 ~/.stCommitMsg 中声明
type:
subject:- type: 本次提交的类型
update: 更新add: 增加新功能 (小)feature: 增加新功能 (大)fix: 修复bugstyle: 代码格式改变opt: 优化doc: 修改文档test: 增加测试代码revert: 撤销上一次的commitbuild: 构建工具或构建过程等的变动, 如:gulp换成了webpack,webpack升级等adapt: 代码适配, 适配其他组件或工具chore: 构建任务更新, 程序包管理器配置等, 生产代码无变动
description: 是对本次提交的简短描述.
不超过 50 个字符.
推荐以动词开头, 如:
设置,修改,增加,删减,撤销等
[Fix #42] Fix table view cell text overflow: GitHub 上通过 commit 信息来关闭相关 issue, 或在末尾加上 (#42) 达到相同效果
删除或创建 origin/HEAD
有时操作 git 发生意外后, git 会提示找不到 orgin/HEAD, 这时我们需要按照提示删除 / 创建
git update-ref -d refs/remotes/origin/HEAD: 删除git symbolic-ref refs/remotes/origin/HEAD refs/remotes/origin/main: 创建
在所有历史中删除某个文件
# 1. 在所有 commit 中删除某个文件
git filter-branch --force --index-filter 'git rm --cached -r --ignore-unmatch /Users/hanley/.local/bin/robot' --prune-empty --tag-name-filter cat -- --all
# 2. 将远端的 HEAD 指向删除 (这是为了给后面删除不用的空间做准备)
git update-ref -d refs/original/refs/heads/master
# 可选: rm -rf .git/refs/original/
# 3. 将所有没有被索引到的文件标记为过期
git reflog expire --expire=now --all
# 4. 将所有过期文件删除
git gc --aggressive --prune=now一些有用的 git alias
将下面这些命令放到 ~/.gitconfig 中
[alias]
root = rev-parse --show-toplevel
lg = log --pretty=format:'%C(bold red)%h%Creset -%C(bold green)%d %C(bold yellow)%s %Creset- %C(red)%cd %Creset- %C(dim green)%an' --date=format:'%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S' --abbrev-commit --graph --all
sdiff =!git diff && git submodule foreach 'git diff'
supdate = submodule update --rebase --init --recursive
spull =!git pull --rebase --recursive
changelog = log origin..HEAD --format='* %s%n%w(,4,4)%+b'
workon = "!f(){ git fetch && git checkout -b \"$1\" $(git symbolic-ref refs/remotes/origin/HEAD | sed \"s@^refs/remotes/@@\"); };f"
refresh = "!f(){ git fetch && git stash && git rebase $(git symbolic-ref refs/remotes/origin/HEAD | sed \"s@^refs/remotes/@@\") && git stash pop; };f"将以下代码放到 ~/.zshrc / ~/.bashrc 中 (理论上下面的这些代码也都可以写成上面的这种形式, 这里只是提供下不同的思路)
alias reignore='git rm -r --cached . && git add .'
alias whyignore='git check-ignore -v'
alias git-root='cd $(git rev-parse --show-toplevel)'
alias gpm="git push origin master"
alias ungit="find . -name '.git' -exec rm -rf {} \;"commiter 与 author 的区别
Git 的每个 Commit 都有作者 (Author) 跟提交者 (Committer) 两种角色, 每次新增修改刪除档案並使用 git commit 指令存成 Commit, 一开始 Commit 的作者与提交者都是执行提交动作的操作人员, 而作者日期 (AuthorDate) 及提交日期 (CommitDate) 就是执行 git commit 的时间. 但如果 Commit 经过再处理或操作, 提交日期將会更新, 而也可能出现提交者与作者不同的状况. 造成作者 / 作者日期与提交者 / 提交日期不同的常见情境有:
- 执行 Rebase (包含
git pull --rebase) - 执行 Amend 修改 Commit 讯息
- 执行 Cherry-Pick 搬动 Commit
- 产生更新档交付他人套用
总之, 只要 Git 操作导致 Commit ID 改变, 就必须更新提交者及提交日期, 若操作者並非该 Commit 的原始提交者, 便会发生作者与提交者不同的状况. 要观察提交日期与提交者, 除使用 Visual Studio, Source Tree, Git GUI 等 GUI 工具, 用 git show --pretty=fuller commit_id 亦可查看
测试 git 连接时 ssh 的具体验证流程
- 使用
GIT_SSH_COMMAND环境变量控制GIT_SSH_COMMAND="ssh -v" git clone example: verbose modeGIT_SSH_COMMAND="ssh -vvv" git clone example: extra verbose mode
- 配置
.gitconfig文件的core.sshCommandgit config core.sshCommand "ssh -vvv"
从终端中在浏览器中打开当前仓库
- hub:
hub browse - git-open
git open: opens https://github.com/TRACKED_REMOTE_USER/CURRENT_REPO/tree/CURRENT_BRANCHgit open [remote-name]: opens https://github.com/PROVIDED_REMOTE_USER/CURRENT_REPO/tree/CURRENT_BRANCHgit open [remote-name] [branch-name]: opens https://github.com/PROVIDED_REMOTE_USER/CURRENT_REPO/tree/PROVIDED_BRANCHgit open --commit: it opens https://github.com/TRACKED_REMOTE_USER/CURRENT_REPO/commit/2ddc8d4548d0cee3d714dcf0068dbec5b168a9b2git open --suffix pulls: It opens the URL https://github.com/TRACKED_REMOTE_USER/CURRENT_REPO/pullsgit open --issue: opens https://github.com/TRACKED_REMOTE_USER/CURRENT_REPO/issues/123git open --print: It prints the URL https://github.com/TRACKED_REMOTE_USER/CURRENT_REPO/
获取 github 文件链接
- github:
https://github.com/username/project/blob/master/test.json->https://raw.githubusercontent.com/username/project/master/test.json - gitee:
https://gitee.com/username/project/blob/master/data.json->https://gitee.com/username/project/raw/master/data.json
github 在国内的访问速度不是很理想, 建议将仓库同步到 gitee 上之后使用 gitee 下载链接
终端命令 git commit 后, 在 vim 中如何中断 commit 流程?
此时可能已经将内容写入
.git/COMMIT_EDITMSG文件
- 将已经输入的内容删除, 然后
:wq退出, 这时 git 会提示Aborting commit due to empty commit message. - 在 vim 中直接使用
:cq!强制以错误的方式退出
Ref
本博客文章采用 CC 4.0 协议,转载需注明出处和作者。
